In general, the material you require depends on the properties you need. (Synthetic) rubber or Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE's) have both their specific properties.
Resistance
When resistance against UV and Ozone influence is of importance (use of material outside during longer periods), properties of the material can be adapted. Extreme heat or cold? Chemicals? Dutch Dipping can offer any specific resistance on customer demand.
Colour
TPE's are easy to colour: fluorescent, metallic and pearl effect, glow in the dark.
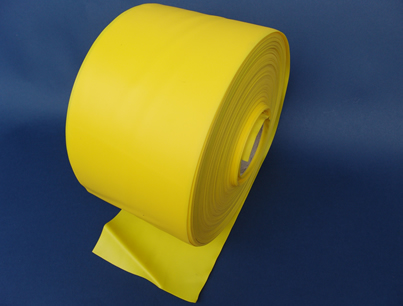
Elastic Sheets
We supply film and sheet in any elastic material. Thickness starts from 0,1 mm to 4 mm, width from 1 mm to 1200 mm.
SEBS sheets:
0,2 till 5 mm wide 1000mm
All colours
Medical
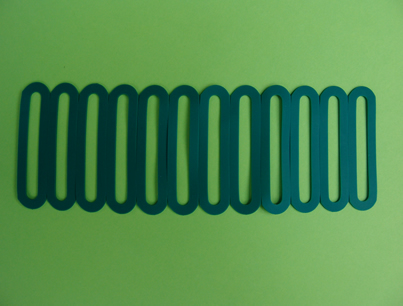
SEBS Rubber bands
4 mm till 120 mm wide on request
All colours
SEBS rubber profile
All models and colours
Send drawing
New developments
No matter how many kilometres of sheet and yarn are produced with us, every new development start with small quantities. Your new development can be produced on our lab equipment. We have performed various consultancy projects for companies in order to support their choice for elastic materials.

Cutting and slitting
We have extensive knowledge in cutting elastic materials to any size or product you need.
Welding
TPE sheet can be easily welded, also to PE or PP material. This avoids the use of glue or tape.
What's the difference between rubber and thermoplastics?
For Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE's), the so-called styrene block copolymers are used, also referred to by the term TPE-S. This is an exceptional basic starting material because a molecule of block copolymers combines the properties of a thermoplastic with those of rubber. This produces a unique type of polymer in which two hard, rigid end-blocks are connected with each other by flexible, elastic mid-block.
This process is also referred to as physical cross-linking. In contrast to chemical cross-linking in the case of vulcanisable rubbers, this process is reversible. When the material is heated to above the Tg of the polystyrene, the domains will soften; at this point, the material can be thermoplastically processed by means of injection moulding, or extrusion, for example. As soon as the temperature returns to below the Tg of the polystyrene, the phase division also returns and the network described above is recreated.
SBS AND SEBS
The end-blocks are polystyrene, which provides the thermoplastic properties of rigidity and flow behaviour. For the elastic mid-block which represents the rubber properties, there are various possibilities but polybutadiene or polyethylene/ butylene are mainly used for this. The material produced in this way is known by the names SBS and SEBS.
Approvals
Various compounds used by Dutchdipping pose approvals for medical applications. The basic polymers comply with the European Pharmacopoeia VI.1.2.2.3 (Polypropylene for Containers for Preparations for Parental Use) or with FDA, Title 21 CFR 177.1810(b)(3). The monomers used in the production of the polymers comply with the requirements of EC Directive 90/128/EEC and its amendments (93/9/EEC and 95/3/EEC) related to Plastic Material and Articles intended to come into contact with foodstuffs. The styrenic resin complies with FDA 177 2600. Skin sensibility studies according to USP Class 6 have been performed on likewise compounds.

